How to Choose the Right Gear Motor for Your Industrial Applications
Choosing the right gear motor for your industrial applications is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the efficiency and performance of your operations. Gear motors, which combine a motor with a gear reducer, offer various advantages, such as increased torque and speed control, making them ideal for a wide range of applications. However, with numerous options available on the market, selecting the appropriate gear motor can be a daunting task. Factors such as load requirements, operating environment, and specific application needs must be carefully considered to ensure optimal functionality. This guide aims to provide essential insights into the key aspects of selecting the right gear motor, empowering you to make informed decisions that enhance your operational success and reliability in demanding industrial settings.
Understanding Your Industrial Application Requirements
When selecting the right gear motor for industrial applications, a comprehensive understanding of specific application requirements is crucial. Start by assessing the operational environment—consider factors such as temperature, exposure to chemicals, and dust or moisture levels. These elements can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the gear motor. Additionally, evaluate the required speed and torque characteristics of the application, as different motors are designed to handle varying loads and rotational speeds. This initial analysis lays the groundwork for selecting a motor that can efficiently meet the demands of your application.
Furthermore, consider the integration of the gear motor within the overall system. Analyze the gear ratio and its compatibility with the driven load to ensure optimal performance. The type of drive (AC or DC), duty cycle, and potential for variable frequency drives (VFDs) should also be factored into your decision. Understanding these parameters will help in selecting a motor that not only fits the technical specifications but is also cost-effective and energy-efficient for sustained operation in industrial settings.
Evaluating Different Types of Gear Motors Available
When evaluating different types of gear motors for industrial applications, it's essential to understand the specific requirements of your project. Gear motors can vary significantly in design, size, and functionality, and these factors impact their performance and suitability for various tasks. The most common types include spur gear motors, planetary gear motors, and worm gear motors, each offering unique benefits. For instance, spur gear motors are known for their simplicity and high efficiency, making them ideal for applications requiring high speed and low torque.
On the other hand, planetary gear motors provide excellent torque output in a compact form factor, which is advantageous in scenarios where space is limited. Worm gear motors offer the advantage of high reduction ratios, allowing for significant torque multiplication, albeit at lower speeds. When choosing the right gear motor, consider load requirements, operational speed, and environmental factors such as temperature and moisture that could affect performance. By conducting a thorough evaluation of these factors and understanding the different types of gear motors available, you can select the most appropriate solution for your specific industrial needs.
Gear Motor Types and Their Efficiency Ratings
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Gear Motor
When selecting the right gear motor for your industrial applications, several key factors come into play. Firstly, it’s crucial to assess the required torque and speed. Understanding the specific load and performance requirements will help ensure that the motor can efficiently meet operational demands. Additionally, evaluating the environment in which the gear motor will operate is essential. Consider factors such as temperature extremes, exposure to moisture or dust, and potential chemical interactions that could affect the motor's longevity and performance.

Another important factor to consider is the gear ratio, which significantly influences the output speed and torque of the motor. A higher gear ratio can provide increased torque but may reduce speed, while a lower ratio can do the opposite. Furthermore, look into the type of gearing system—whether planetary, spur, or worm gears—since each design has its own advantages and limitations in terms of efficiency and noise levels. Finally, factor in maintenance and service life expectations, as well as the overall cost-effectiveness of different gear motors, to ensure you select the most suitable option for your application.
Assessing Power, Speed, and Torque Needs for Applications
When selecting a gear motor for industrial applications, it's crucial to assess the power, speed, and torque requirements specific to your operation. According to a report by the Research and Markets, the global gear motor market was valued at approximately $10 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is driven by increasing automation in industries, which necessitates a better understanding of how gear motors can meet diverse application needs.
Power requirements depend largely on the specific tasks the motor will perform. For example, applications requiring high starting torque, such as conveyor systems, typically need gear motors with a power range of 0.5 to 10 HP. Conversely, lighter applications may function effectively with motors around 0.1 to 0.5 HP. Speed is another critical factor; many applications operate most efficiently at speeds between 100 to 300 RPM. Knowing the optimal torque, which influences the motor's responsiveness and ability to maintain constant speeds under varying loads, is equally important. The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) states that the torque requirements can vary widely, often ranging from 10 to over 100 Nm depending on the specific design of the machinery involved. Understanding these key parameters will ensure that the chosen gear motor aligns efficiently with operational demands.
How to Choose the Right Gear Motor for Your Industrial Applications
| Motor Type |
Rated Power (W) |
Speed (RPM) |
Torque (Nm) |
Efficiency (%) |
Application |
| AC Induction Motor |
1500 |
1450 |
10 |
85 |
Conveyor Systems |
| DC Gear Motor |
250 |
3000 |
4 |
78 |
Robotics |
| Brushless DC Motor |
500 |
4000 |
1.25 |
92 |
CNC Machines |
| Stepper Motor |
100 |
2000 |
0.5 |
80 |
3D Printers |
| Servo Motor |
600 |
5000 |
3.2 |
90 |
Packaging Machines |
Comparing Costs and Maintenance Needs of Gear Motor Options
When selecting a gear motor for industrial applications, understanding the costs associated with different options is essential. Gear motors vary widely in price depending on their size, power, and complexity. Standard models tend to be more affordable, while specialized motors designed for high torque or specific environmental conditions can significantly increase initial expenditure. It’s crucial to evaluate not only the upfront costs but also how these expenses align with your operational budget and long-term goals.
Maintenance needs are another critical factor in the decision-making process. Some gear motors require regular maintenance to ensure optimum performance, which may include lubrication, inspections, and part replacements. On the other hand, gear motors designed for higher efficiency or those made with advanced materials may offer reduced maintenance requirements, leading to lower long-term operational costs. Therefore, businesses must weigh the initial cost against potential savings associated with maintenance, creating a balanced approach that supports both performance and budget considerations.

Home
Products
SIEMENS Gearmotor
 SIEMENS Helical Gearmotor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Helical Gearmotor Low Voltage  SIEMENS Bevel Helical Gearmotor
SIEMENS Bevel Helical Gearmotor  SIEMENS Parallel Shaft Gearmotor
SIEMENS Parallel Shaft Gearmotor  SIEMENS Worm Gearmotor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Worm Gearmotor Low Voltage  SIEMENS With Servo Motor Gearmotor
SIEMENS With Servo Motor Gearmotor  SIEMENS Low Voltage Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Low Voltage Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS High Voltage Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS High Voltage Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS Marine Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Marine Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS Servo Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Servo Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS S210 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S210 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS S150 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S150 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS S120 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S120 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS G130/G150
SIEMENS SINAMICS G130/G150  SIEMENS SINAMICS G120 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS G120 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS G120C Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS G120C Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS V90
SIEMENS SINAMICS V90  SIEMENS SINAMICS V70 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS V70 Low Voltage  FLENDER Gear Unit
FLENDER Gear Unit  FLENDER Helical Gear Unit
FLENDER Helical Gear Unit  Flender gear units for lifting and luffing gears
Flender gear units for lifting and luffing gears  FLENDER Gear Unit gearunit gearbox
FLENDER Gear Unit gearunit gearbox  Optimal Drive Solution For Maximum Performance
Optimal Drive Solution For Maximum Performance  Strongly operating against biodegradable constituents
Strongly operating against biodegradable constituents  SINGLE SCREW Special industry dedicated gearunit gearbox
SINGLE SCREW Special industry dedicated gearunit gearbox  Playmaker In The Premium League
Playmaker In The Premium League  Conveyor belts gearunit gearbox
Conveyor belts gearunit gearbox  Paper And Pulp Preparation Sections
Paper And Pulp Preparation Sections  Operational Reliability Even In Case Of The Highest Ventilation Forces
Operational Reliability Even In Case Of The Highest Ventilation Forces  Reliable Gear Units For High Performance Vertical Conveyors 59/200
Reliable Gear Units For High Performance Vertical Conveyors 59/200  Maximum power density – PLANUREX 3 L individual drives for your sugar cane mill
Maximum power density – PLANUREX 3 L individual drives for your sugar cane mill  The proven all rounder gearunit gearbox
The proven all rounder gearunit gearbox  Stirs and stirs and stirs gearunit gearbox
Stirs and stirs and stirs gearunit gearbox  Flexibility on Board gearunit gearbox
Flexibility on Board gearunit gearbox  The right gearbox for all Multi-Engine Ships
The right gearbox for all Multi-Engine Ships  Reliable Power Generation on board
Reliable Power Generation on board  Maximum performance level, fast deliverable
Maximum performance level, fast deliverable  Efficient and compact – FLENDER Gear Units for Sugar Mills
Efficient and compact – FLENDER Gear Units for Sugar Mills  Extremely strong. Extremely compact. Extremely stressable.
Extremely strong. Extremely compact. Extremely stressable.  FLENDER Coupling
FLENDER Coupling  ZAPEX ZW Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling
ZAPEX ZW Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling  ZAPEX ZN Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling
ZAPEX ZN Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling  N-EUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling
N-EUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling  N-ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling
N-ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling 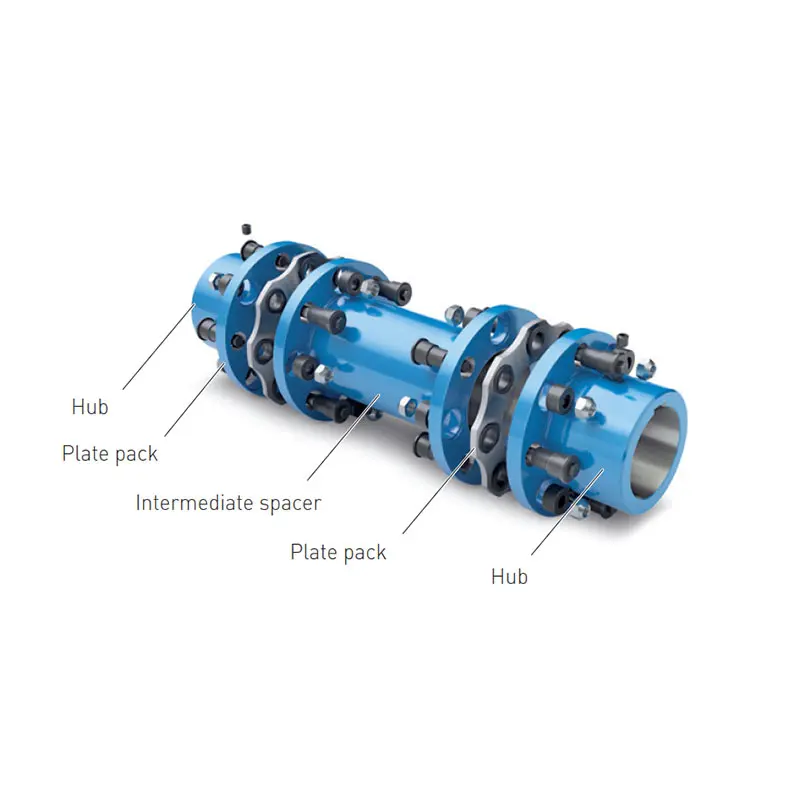 ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling Spare and Parts
ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling Spare and Parts  N-EUPEX DS Flexible High Performance Coupling
N-EUPEX DS Flexible High Performance Coupling  RUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling
RUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling  N BIPEX Flexible high performance coupling
N BIPEX Flexible high performance coupling  ELPEX B Highly Flexible Coupling
ELPEX B Highly Flexible Coupling  ELPEX S Highly Flexible Coupling high performance
ELPEX S Highly Flexible Coupling high performance  ELPEX Highly Flexible Coupling high performance
ELPEX Highly Flexible Coupling high performance  FLUDEX Fluid Coupling high performance
FLUDEX Fluid Coupling high performance  SIPEX Backlash free Coupling high performance
SIPEX Backlash free Coupling high performance  BIPEX S Backlash free Coupling high performance
BIPEX S Backlash free Coupling high performance  FLENDER Coupling Spare Parts high performance
FLENDER Coupling Spare Parts high performance  SEW Gearmotor
SEW Gearmotor
Our Company
News
Case
Contact Us
 R Series Helical Gearmotor low voltage
R Series Helical Gearmotor low voltage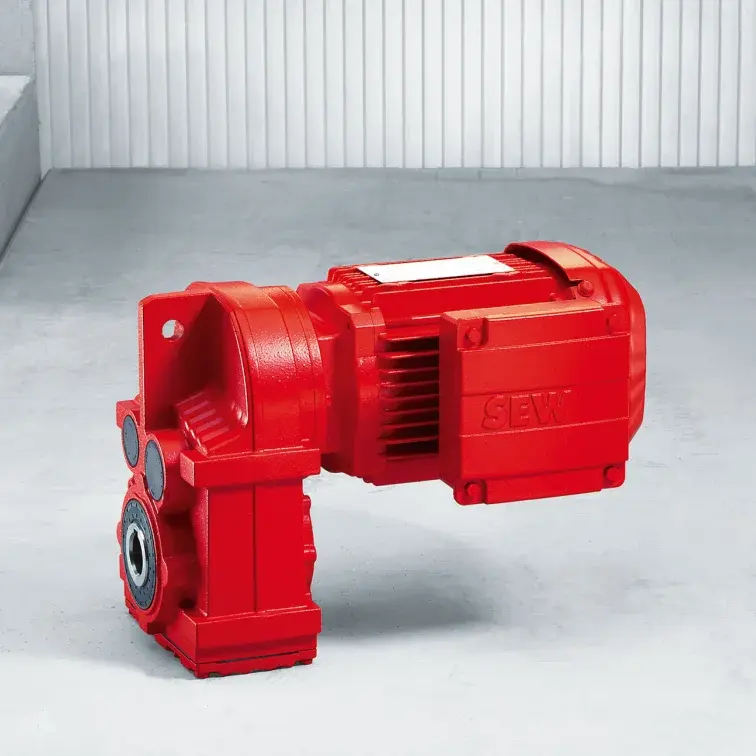 F Series Parallel Shaft Gearmotor low voltage
F Series Parallel Shaft Gearmotor low voltage K Series Helical Bevel Gearmotor low voltage
K Series Helical Bevel Gearmotor low voltage S Series Helical Worm Gearmotor low voltage
S Series Helical Worm Gearmotor low voltage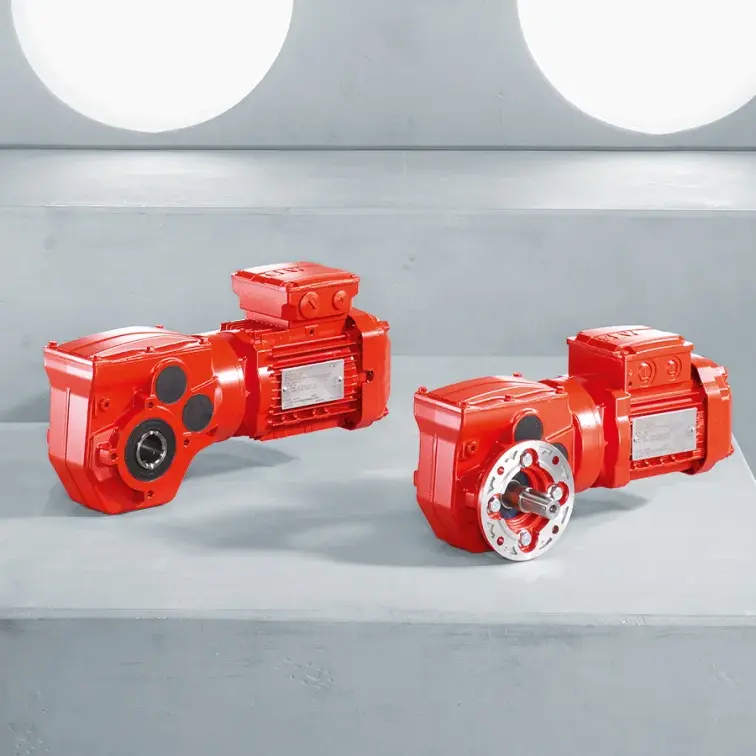 W Series SPIROPLAN® Right Angle Gearmotor
W Series SPIROPLAN® Right Angle Gearmotor