Understanding Gear Motors and Their Applications in Industry
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial automation, gear motors have emerged as pivotal components influencing operational efficiency across various sectors. According to a recent report by Research and Markets, the global gear motor market is projected to reach $13 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions in manufacturing processes. Gear motors combine high torque output with compact design, making them essential for applications ranging from conveyor systems to robotics. As industries strive to enhance productivity and reduce downtime, understanding the functionality and diverse applications of gear motors becomes paramount. This blog aims to delve into the intricacies of gear motors, exploring their construction, types, advantages, and the integral roles they play in modern industrial settings.
Overview of Gear Motors: Definition, Types, and Components
Gear motors are essential components in various industrial applications, converting electrical energy into mechanical power with optimal efficiency. Understanding the definition, types, and components of gear motors is crucial for selecting the right one for specific tasks. Typically, gear motors consist of an electric motor coupled with a gear reduction unit, allowing for increased torque output and reduced speed, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
When choosing a gear motor, consider the application requirements such as speed, torque, and size. It is vital to match the motor's specifications with the operational demands of your project to ensure optimal performance.
**Tips:** Always check the gear ratio of the motor, as it directly affects the output speed and torque. Additionally, consider the duty cycle of your application to choose a motor that can handle continuous versus intermittent operation. Lastly, ensure proper heat dissipation to maintain the gear motor's efficiency and longevity.
Key Performance Metrics: Torque, Speed, and Efficiency in Gear Motors
When it comes to gear motors, three key performance metrics stand out: torque, speed, and efficiency. Torque, the measure of rotational force, is crucial in determining a gear motor's ability to perform specific tasks. High torque is essential for applications requiring heavy-load movements, such as in industrial machinery and conveyor systems. Understanding the required torque for your application can directly influence the selection of the appropriate gear motor, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Speed, on the other hand, relates to how quickly the motor can rotate its output shaft. Different applications necessitate varying speeds; for instance, assembly lines may require faster speeds to maintain productivity, whereas precision tasks might need slower, more controlled movements. It’s also vital to consider how speed and torque interact, as increasing one often leads to a decrease in the other, a relationship governed by the motor’s characteristics.
Efficiency is another critical factor; it measures how effectively the gear motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Higher efficiency means reduced energy consumption and less heat generation, which can prolong the motor's lifespan and lower operational costs. Selecting a gear motor with a high-efficiency rating can be a significant advantage in industries focused on sustainability and reducing overall energy expenditures. By understanding these key performance metrics, businesses can better tailor their gear motor choices to meet operational demands.

Industrial Applications: How Gear Motors Drive Automation Across Sectors
Gear motors are pivotal in driving automation across various industrial sectors, significantly improving efficiency and productivity. According to a market research report by Allied Market Research, the global gear motor market is projected to reach $32.1 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2020. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on gear motors in applications ranging from material handling systems to robotic automation.
In manufacturing, for example, gear motors facilitate precise control of equipment, enhancing production rates and quality. The food and beverage sector, which alone accounted for 23% of the overall gear motor market in 2020, utilizes these motors for tasks such as conveyor systems and packaging machinery. Additionally, the automotive industry is adopting gear motors for electric vehicles (EVs), where they are essential for driving various functionalities including steering and braking systems. With their ability to offer high torque in a compact form factor, gear motors are essential drivers of automation, allowing industries to maintain competitive advantages in an increasingly automated world.

Selecting the Right Gear Motor: Factors to Consider for Optimal Performance
When selecting the right gear motor for industrial applications, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance. Firstly, it is essential to assess the torque requirements of your specific application. Different tasks demand varying torque levels, and understanding the load conditions will guide you in choosing a gear motor that can efficiently handle those demands without risk of overheating or failure.
Another critical factor to evaluate is the motor's speed characteristics. Depending on the needs of your machinery, you may require a gear motor with constant speed or one capable of variable speed. Analyzing the operational environment is also vital; factors such as temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to dust or corrosive substances can all influence the selection process. By considering these elements, you can ensure that the gear motor chosen will not only meet the technical requirements but also provide durability and reliability over time in demanding industrial settings.
Understanding Gear Motors and Their Applications in Industry - Selecting the Right Gear Motor: Factors to Consider for Optimal Performance
| Parameter |
Description |
Importance |
| Torque |
The rotational force the motor can provide. |
Critical for determining load capacity and performance. |
| Speed |
The maximum rotation speed of the motor in RPM. |
Affects the operational efficiency and application compatibility. |
| Efficiency |
Ratio of output power to input power. |
High efficiency reduces operating costs and heat generation. |
| Form Factor |
Physical dimensions and mounting style of the motor. |
Determines fit within equipment and ease of installation. |
| Load Characteristics |
Type of load (static, dynamic) the motor will drive. |
Essential for selecting a motor that can handle specific applications. |
| Control Method |
Type of control (analog, digital, servo) for the motor. |
Influences motor responsiveness and integration into systems. |
| Duty Cycle |
The operational time versus rest time for the motor. |
Important for ensuring longevity and preventing overheating. |
| Reference Material |
User manuals and technical specifications guide motor selection. |
Helps in aligning motor attributes with application needs. |
Future Trends: Innovations in Gear Motor Technology and Industry Impact
The evolution of gear motors has been significantly shaped by innovations that enhance efficiency and performance across various industries. One of the most notable trends is the integration of smart technology, enabling gear motors to communicate with other machinery. This connectivity allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, ultimately reducing downtime and operational costs. With Industry 4.0 on the rise, manufacturers are increasingly adopting IoT-enabled gear motors that provide valuable data insights, helping optimize processes and improve decision-making.
Another emerging trend is the focus on energy efficiency and sustainability. As environmental regulations become stricter, companies are seeking gear motors that not only deliver high performance but also minimize energy consumption. Innovations such as advanced materials and design techniques are helping to produce lightweight, energy-efficient motors. Furthermore, developments in regenerative braking systems allow for energy recovery during operation, marking a significant step toward greener industrial practices. The future of gear motor technology looks promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at pushing the boundaries of what is possible in industrial applications.

Home
Products
SIEMENS Gearmotor
 SIEMENS Helical Gearmotor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Helical Gearmotor Low Voltage  SIEMENS Bevel Helical Gearmotor
SIEMENS Bevel Helical Gearmotor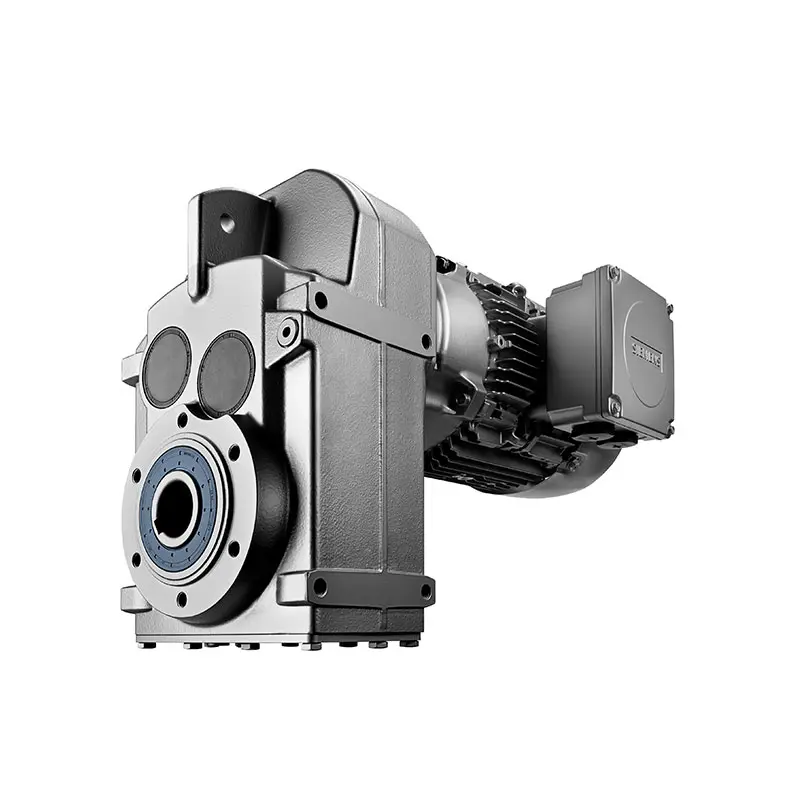  SIEMENS Parallel Shaft Gearmotor
SIEMENS Parallel Shaft Gearmotor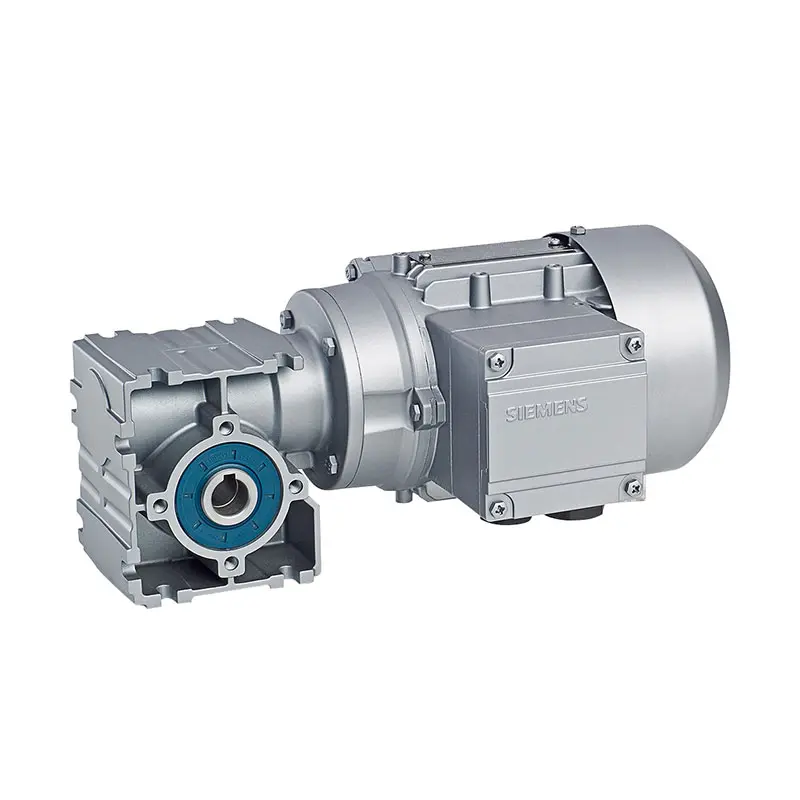  SIEMENS Worm Gearmotor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Worm Gearmotor Low Voltage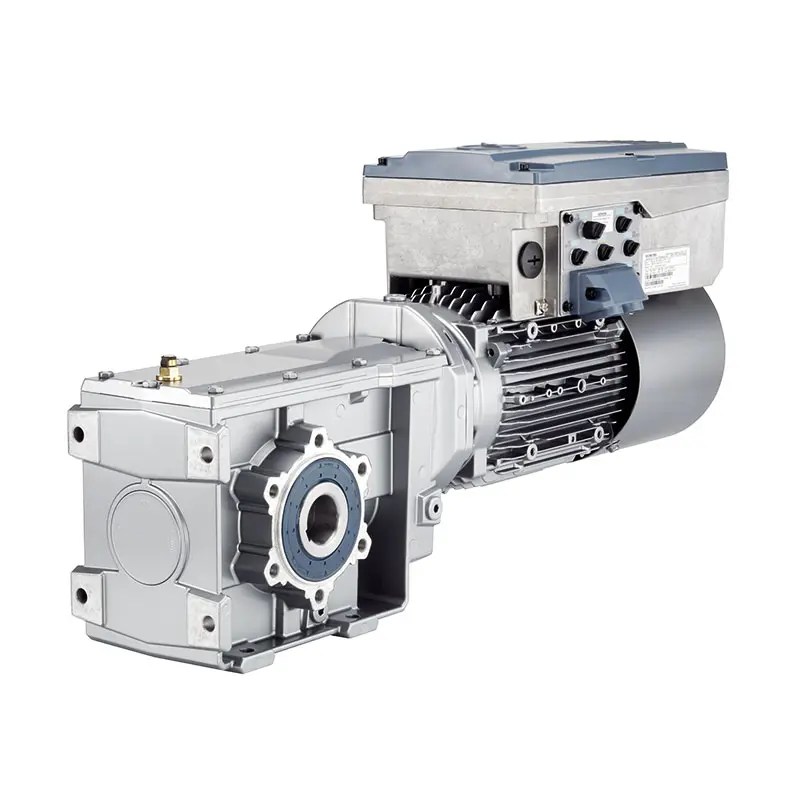  SIEMENS With Servo Motor Gearmotor
SIEMENS With Servo Motor Gearmotor  SIEMENS Low Voltage Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Low Voltage Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS High Voltage Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS High Voltage Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS Marine Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Marine Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS Servo Motor Low Voltage
SIEMENS Servo Motor Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS S210 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S210 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS S150 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S150 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS S120 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS S120 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS G130/G150
SIEMENS SINAMICS G130/G150  SIEMENS SINAMICS G120 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS G120 Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS G120C Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS G120C Low Voltage  SIEMENS SINAMICS V90
SIEMENS SINAMICS V90  SIEMENS SINAMICS V70 Low Voltage
SIEMENS SINAMICS V70 Low Voltage  FLENDER Gear Unit
FLENDER Gear Unit  FLENDER Helical Gear Unit
FLENDER Helical Gear Unit  Flender gear units for lifting and luffing gears
Flender gear units for lifting and luffing gears  FLENDER Gear Unit gearunit gearbox
FLENDER Gear Unit gearunit gearbox  Optimal Drive Solution For Maximum Performance
Optimal Drive Solution For Maximum Performance  Strongly operating against biodegradable constituents
Strongly operating against biodegradable constituents  SINGLE SCREW Special industry dedicated gearunit gearbox
SINGLE SCREW Special industry dedicated gearunit gearbox  Playmaker In The Premium League
Playmaker In The Premium League  Conveyor belts gearunit gearbox
Conveyor belts gearunit gearbox  Paper And Pulp Preparation Sections
Paper And Pulp Preparation Sections  Operational Reliability Even In Case Of The Highest Ventilation Forces
Operational Reliability Even In Case Of The Highest Ventilation Forces  Reliable Gear Units For High Performance Vertical Conveyors 59/200
Reliable Gear Units For High Performance Vertical Conveyors 59/200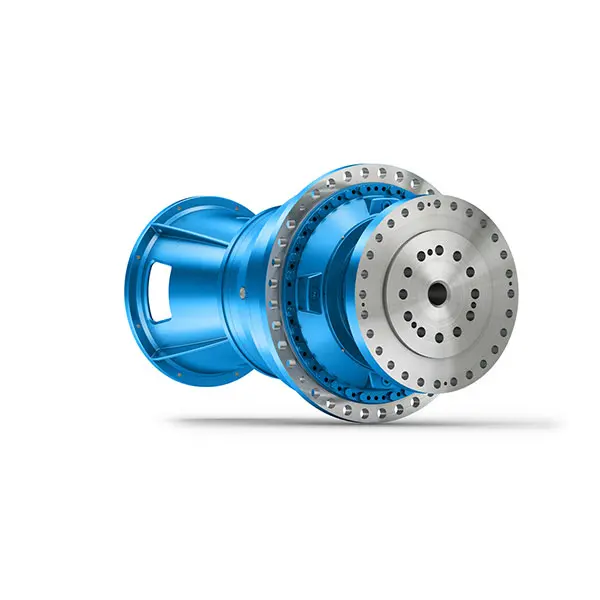  Maximum power density – PLANUREX 3 L individual drives for your sugar cane mill
Maximum power density – PLANUREX 3 L individual drives for your sugar cane mill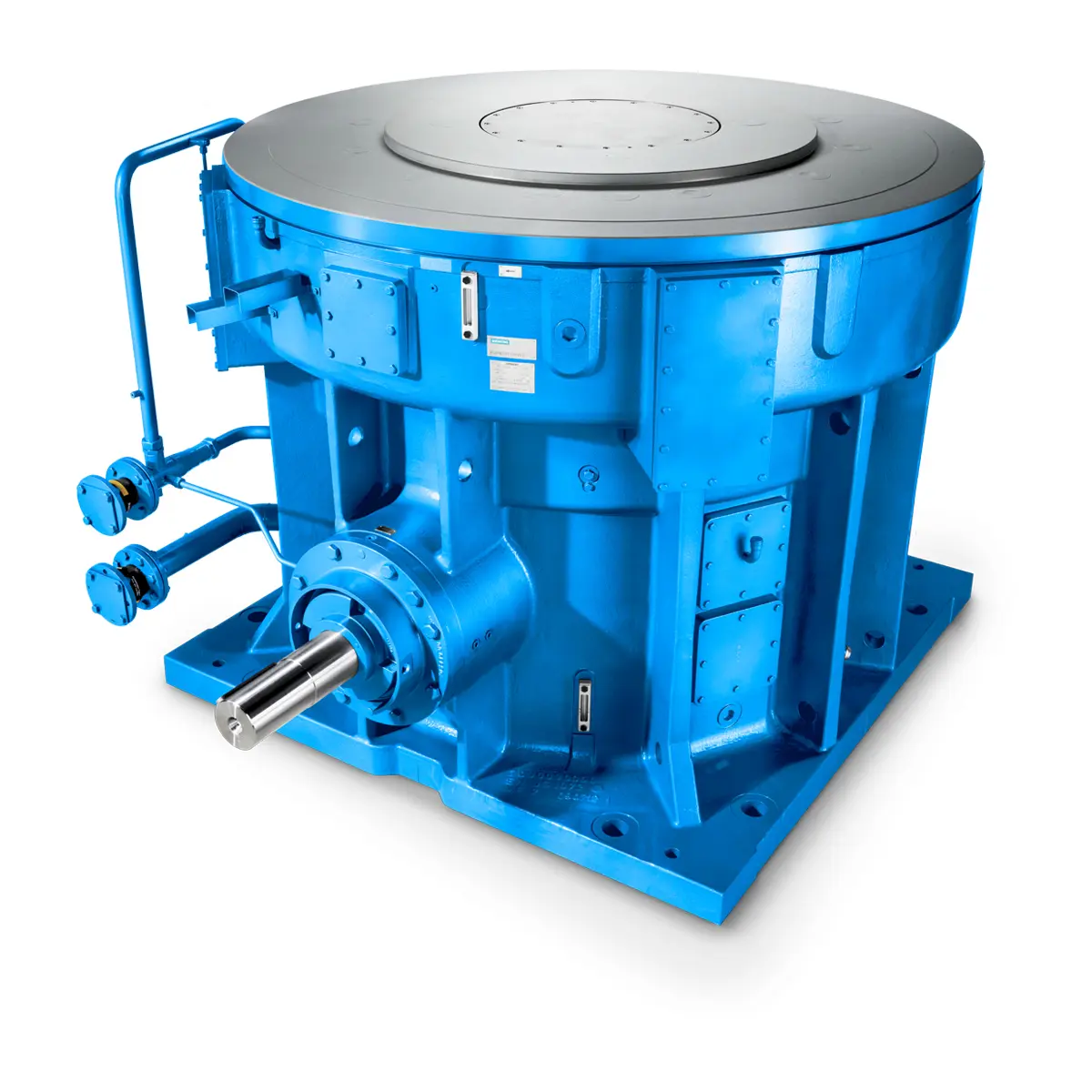  The proven all rounder gearunit gearbox
The proven all rounder gearunit gearbox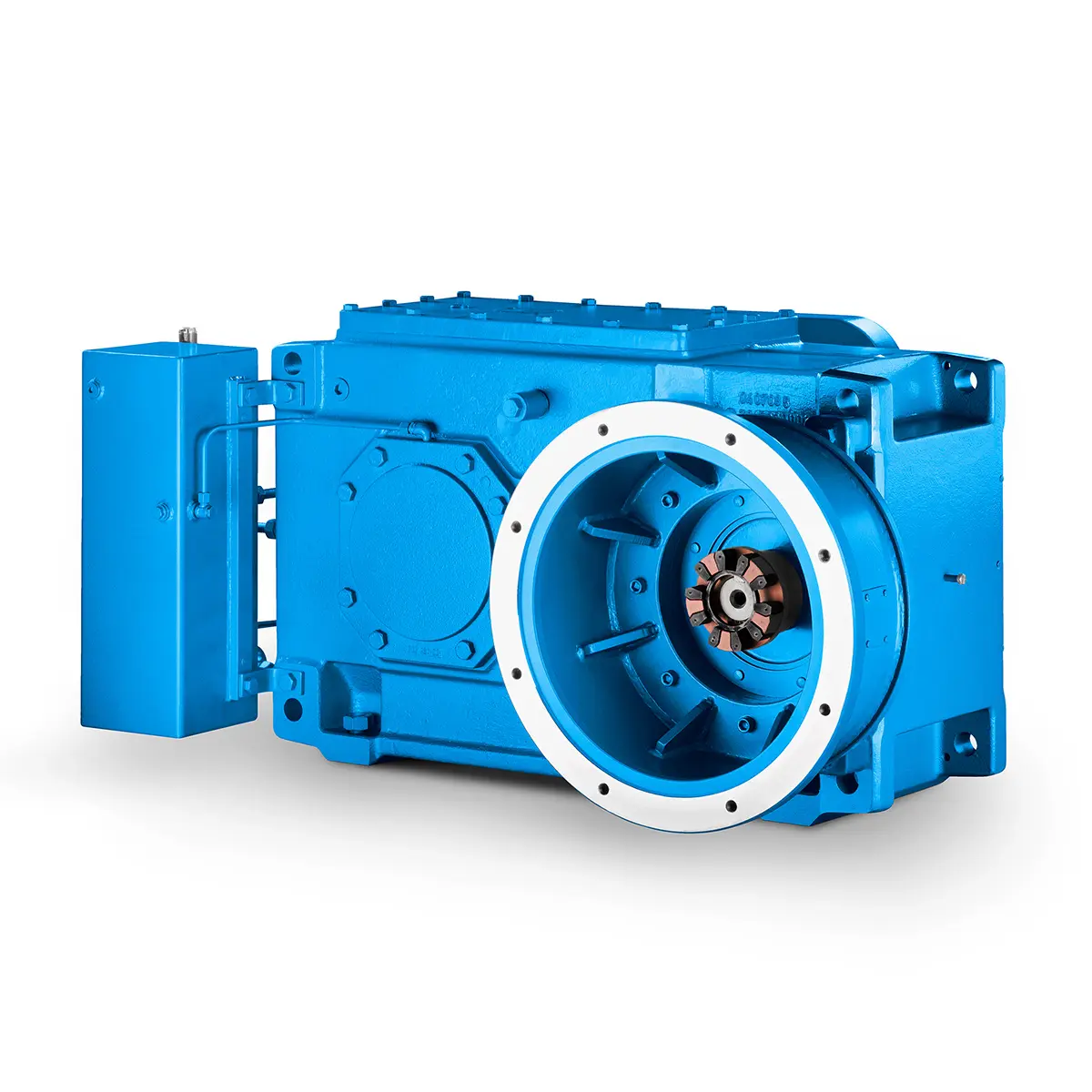  Stirs and stirs and stirs gearunit gearbox
Stirs and stirs and stirs gearunit gearbox  Flexibility on Board gearunit gearbox
Flexibility on Board gearunit gearbox  The right gearbox for all Multi-Engine Ships
The right gearbox for all Multi-Engine Ships  Reliable Power Generation on board
Reliable Power Generation on board  Maximum performance level, fast deliverable
Maximum performance level, fast deliverable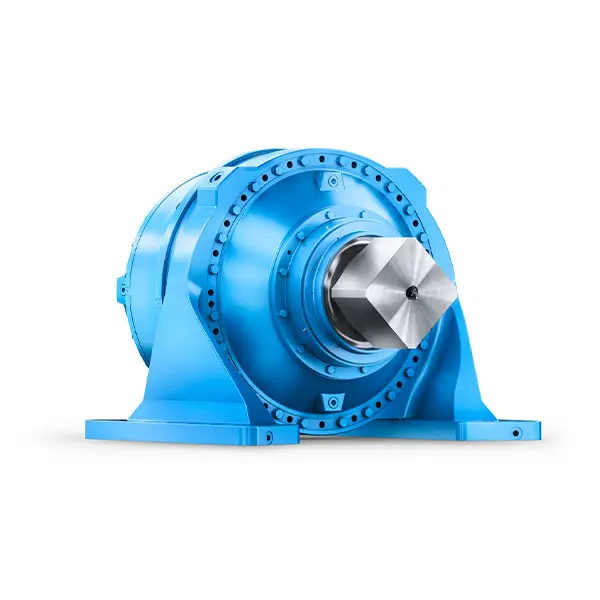  Efficient and compact – FLENDER Gear Units for Sugar Mills
Efficient and compact – FLENDER Gear Units for Sugar Mills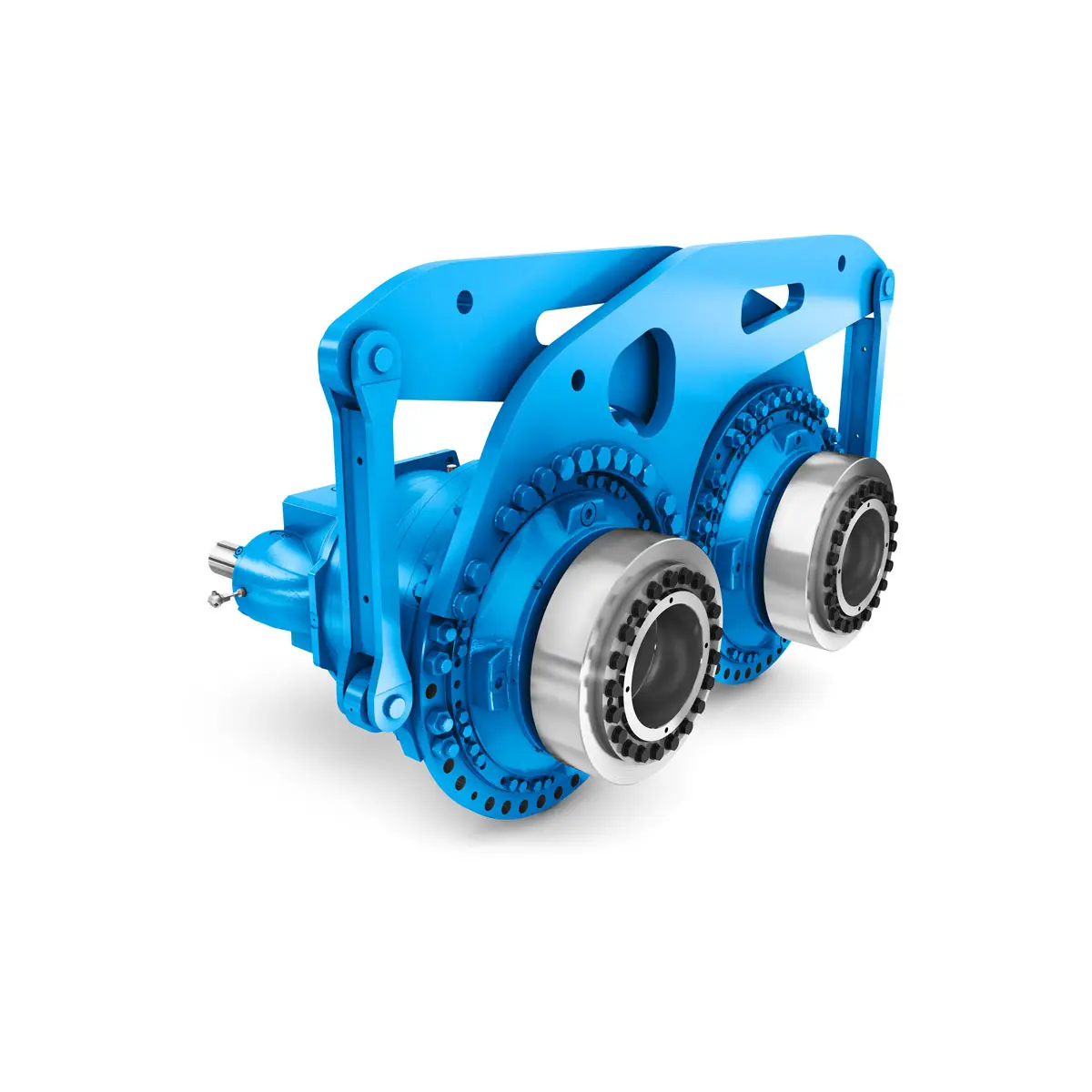  Extremely strong. Extremely compact. Extremely stressable.
Extremely strong. Extremely compact. Extremely stressable.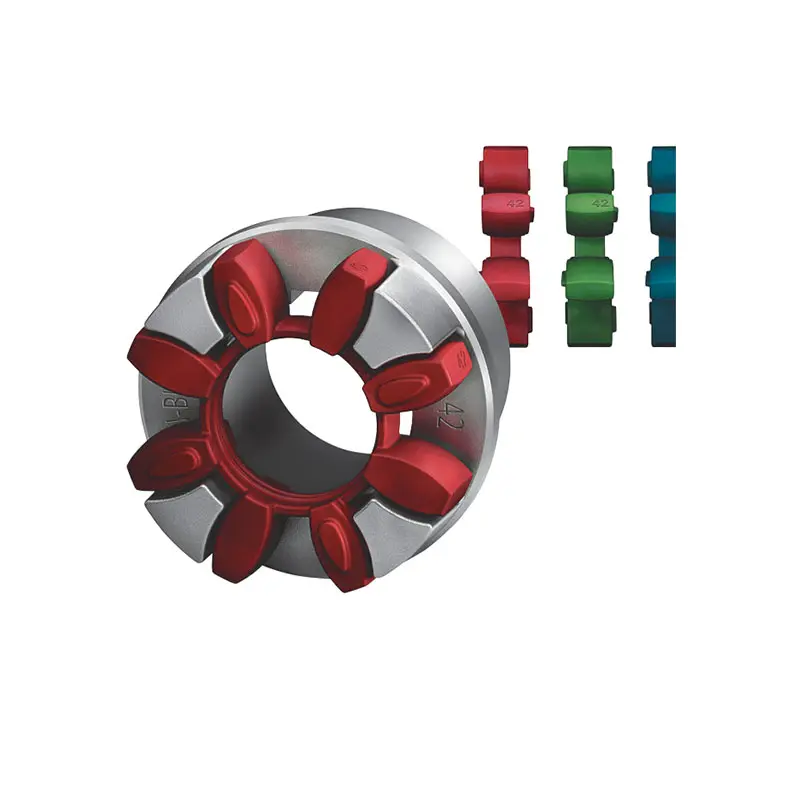  FLENDER Coupling
FLENDER Coupling  ZAPEX ZW Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling
ZAPEX ZW Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling  ZAPEX ZN Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling
ZAPEX ZN Torsionally Rigid Gear Coupling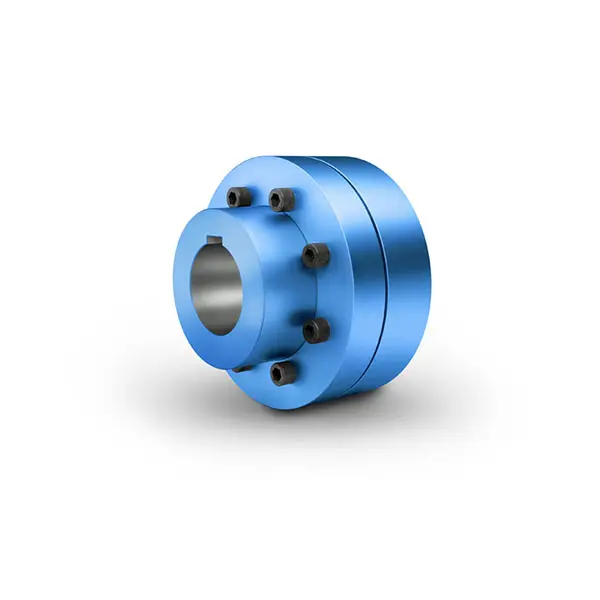  N-EUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling
N-EUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling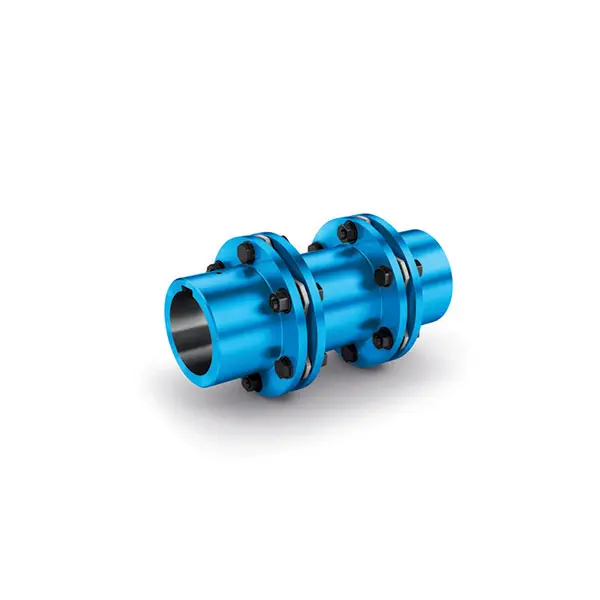  N-ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling
N-ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling 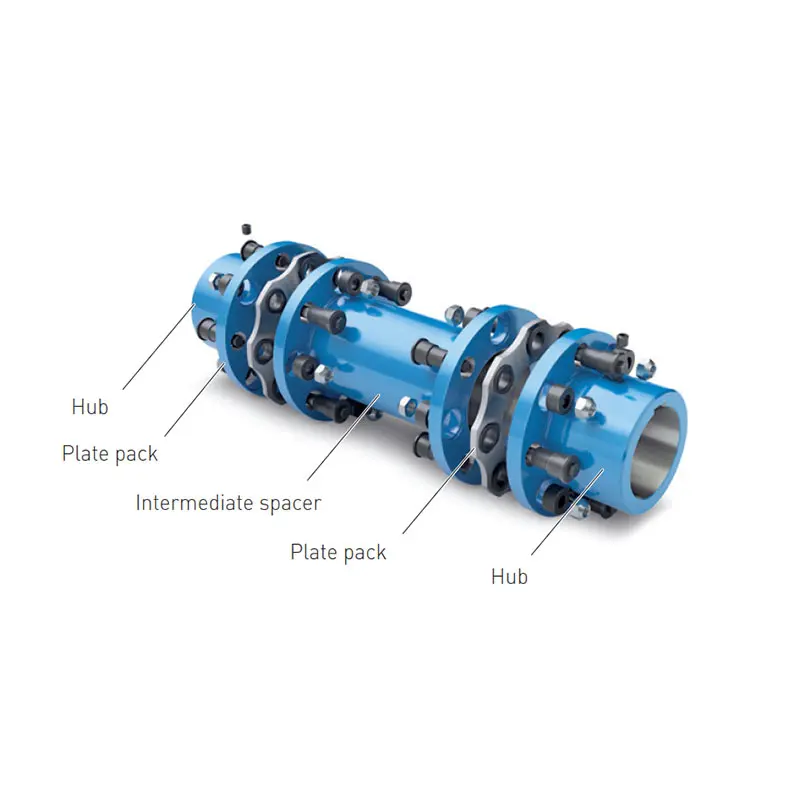 ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling Spare and Parts
ARPEX Torsionally Rigid All-Steel Coupling Spare and Parts  N-EUPEX DS Flexible High Performance Coupling
N-EUPEX DS Flexible High Performance Coupling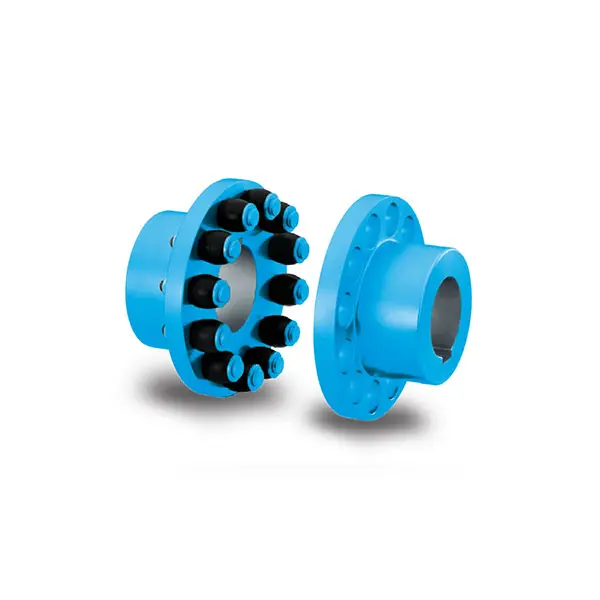  RUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling
RUPEX Flexible high performance Coupling 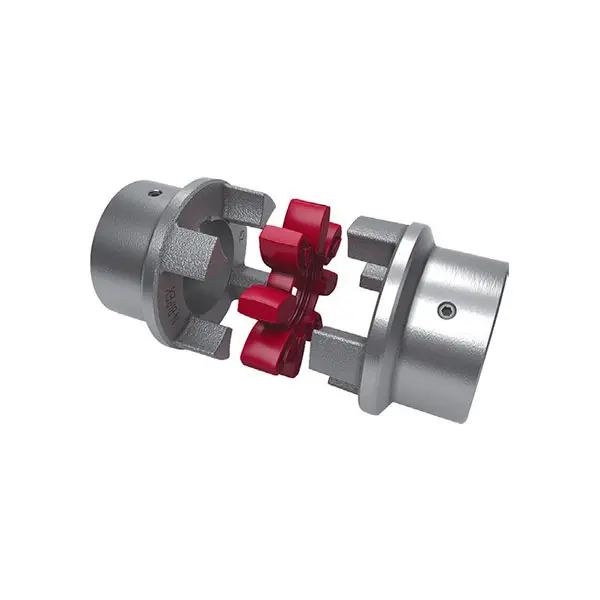 N BIPEX Flexible high performance coupling
N BIPEX Flexible high performance coupling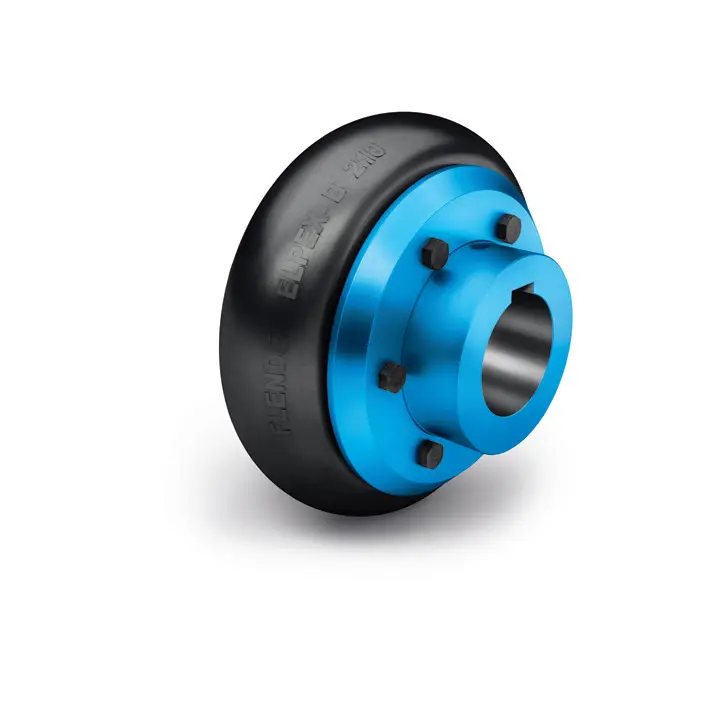  ELPEX B Highly Flexible Coupling
ELPEX B Highly Flexible Coupling  ELPEX S Highly Flexible Coupling high performance
ELPEX S Highly Flexible Coupling high performance  ELPEX Highly Flexible Coupling high performance
ELPEX Highly Flexible Coupling high performance  FLUDEX Fluid Coupling high performance
FLUDEX Fluid Coupling high performance  SIPEX Backlash free Coupling high performance
SIPEX Backlash free Coupling high performance  BIPEX S Backlash free Coupling high performance
BIPEX S Backlash free Coupling high performance  FLENDER Coupling Spare Parts high performance
FLENDER Coupling Spare Parts high performance  SEW Gearmotor
SEW Gearmotor
Our Company
News
Case
Contact Us
 R Series Helical Gearmotor low voltage
R Series Helical Gearmotor low voltage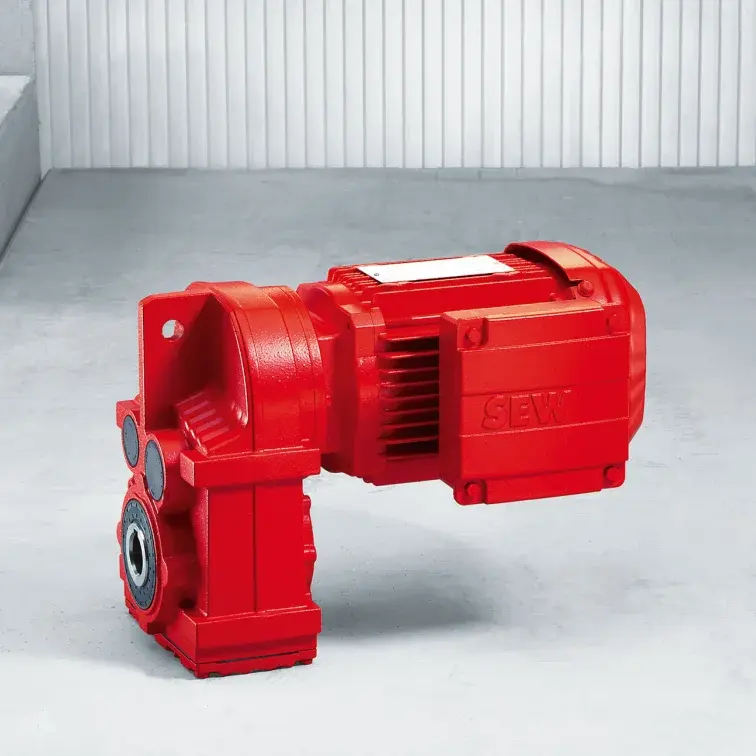 F Series Parallel Shaft Gearmotor low voltage
F Series Parallel Shaft Gearmotor low voltage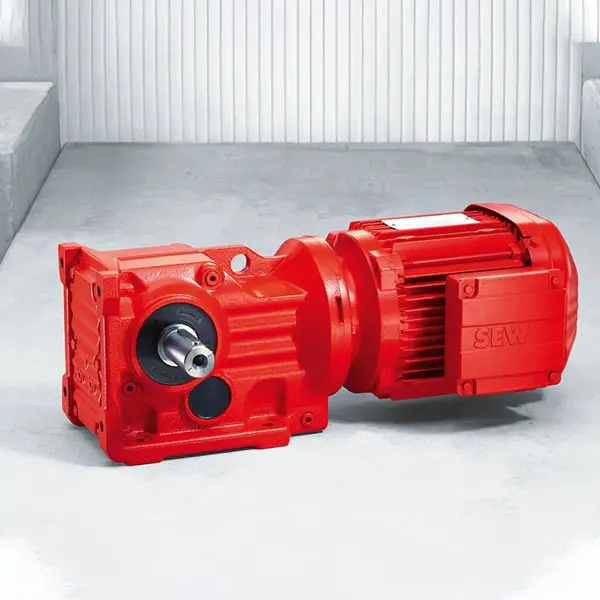 K Series Helical Bevel Gearmotor low voltage
K Series Helical Bevel Gearmotor low voltage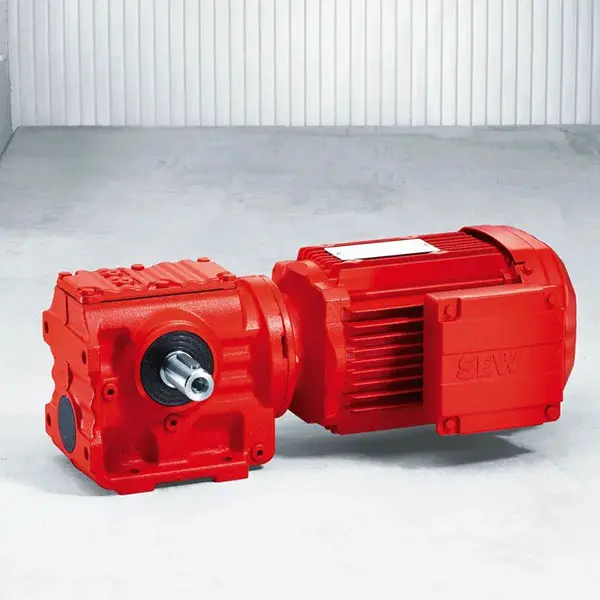 S Series Helical Worm Gearmotor low voltage
S Series Helical Worm Gearmotor low voltage W Series SPIROPLAN® Right Angle Gearmotor
W Series SPIROPLAN® Right Angle Gearmotor